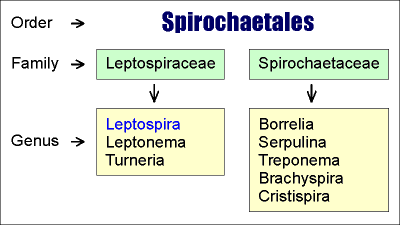
Principles of Leptospira classification
| The genus Leptospira belongs to the family leptospiraceae, order Spirochateales. Two types of classification coexist, one based on genetic and one based on antigenic determinants. Both recognize patogenic and saprophytic species, but serologically indistiguishable strains may belong to totaly different species according to genetic classification. |  |
| . | Leptospira | Leptonema | Treponema | Serpulina | Borrelia |
| Obligate aerobes | + | + | - | - | - |
| Obligate anaerobes | - | - | S | + | - |
| Facultative aerobes | - | - | - | - | - |
| Microaerophiles | + | - | - | - | S |
| Cell dia. um | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1-0.4 | 0.3-0.4 | 0.2-0.5 |
| Cell length um | 6-24 | 6-20 | 5-20 | 7-9 | 3-20 |
| Energy and carbon sources | |||||
| Carbohydrates | - | - | S | + | + |
| Long-chain fatty acids | + | + | - | - | + |
| Growth on Tryptose blood agar | + | + | |||
| Presence of intracytoplasmic tubules | - | + | + | + | - |
| Chromosomal G+C content mol%* | 35-41 | 51-53 | |||
(*) Hovind-Hougen K.; Leptospiraceae, a new family
to include Leptospira Noguchi 1917 and Leptonema ge. nov.; Int. J. of Sys.
Bacteriol. 29:245-251, 1979.
(**) Bergey Manual of Determinative Bacteriology - Ninth
Edition - Williams and Wilkins, 1994.
| Characteristic |
|
|
| Patogenicity |
|
|
| Growth at 13 C |
|
|
| Inhibition of growth with 8'azaguanine |
|
|
| Conversion to spherical phorms by 1M NaCl |
|
|
| Lipase |
|
|
| Mol% G+C of DNA |
|
|